- He tried to change the configuration himself and now his network settings are completely messed up. I can't even get into the network utility to change it. So, I am looking for the network configuration files from the command line for leopard and tiger.
- If not, plug an Ethernet lead between your Mac and the router to check the network name. With Apple routers, open AirPort Utility and look in the Airport Wireless tab, or if you have a third.
- Nic tap,mac=02:ca:fe:f0:0d:01 Network Monitoring. You can monitor the network configuration using info network and info usernet commands. You can capture network traffic from within QEMU using the filter-dump object, like this: -netdev user,id=u1 -device e1000,netdev=u1 -object filter-dump,id=f1,netdev=u1,file=dump.dat.
- The ability to switch between different sets of network settings (locations) can be useful in circumstances such as these: You use the same type of network (such as Ethernet) at work and at home, but the settings you use at work don't allow your Mac to automatically connect to the same type of network at home.
The ability to switch between different sets of network settings (locations) can be useful in circumstances such as these:
- You use the same type of network (such as Ethernet) at work and at home, but the settings you use at work don't allow your Mac to automatically connect to the same type of network at home.
- Your Mac connects to more than one type of network service (such as both Wi-Fi and Ethernet) at work and at home, but at work you want your Mac to try connecting to the Ethernet network first, and at home you want your Mac to try connecting to the Wi-Fi network first. In other words, you want to set a different service order for each location.
- Your Mac isn't connecting to your network and you want to quickly reset your network settings for testing purposes, without losing your current network settings.

Your network settings can be accessed using some common terminal commands that, for the most part, require very little configuration to use. We still recommend you use the System Preferences app for configuration (unless you’re happy using the terminal), but identifying your Mac terminal network settings is easy.
In each of these examples, the Location feature of Network preferences can help.
How to add or remove a network location
- Choose Apple menu () > System Preferences, then click Network.
- The Location pop-up menu shows the name of your currently selected set of network settings. The default location is named Automatic. Choose Edit Locations from this menu.
- Click the Add (+) button below the list of locations, then type a name for the new location, such as Work or Home or Mobile. (To remove a location, use the Remove (–) button below the list.)
- Click Done. The Location menu should now show the name of your new location. Any changes you now make to your Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or other network settings will be saved to that location when you click Apply. The network settings in your previous location remain as you left them, so you can use the Location menu to switch back at any time.
- Click Apply to save your settings and complete the switch from the previous location to the new one. Your Mac then automatically tries to determine the correct settings for each type of network. If you need to change the settings manually, remember to click Apply again after making your changes.
How to switch between network locations
If you have more than one location, you can use either of these methods to switch between them:
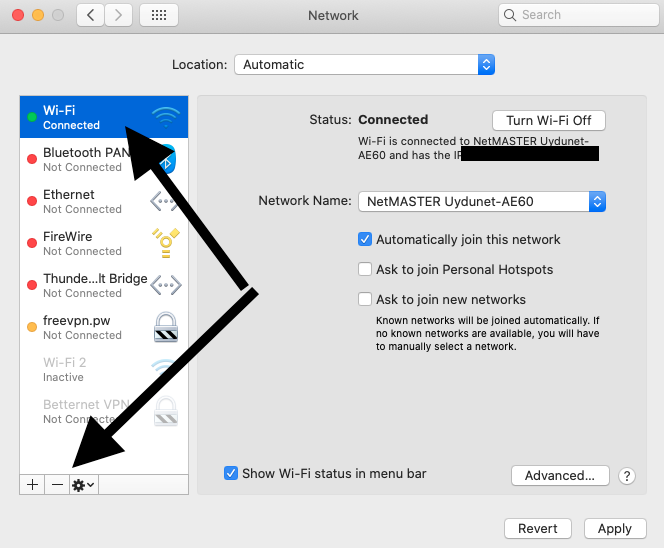
- Use the Location pop-up menu in Network preferences, as described above. Remember to click Apply after choosing a location.
- Or choose Apple menu > Location from the menu bar, then choose your location from the submenu.
How to change the network service order
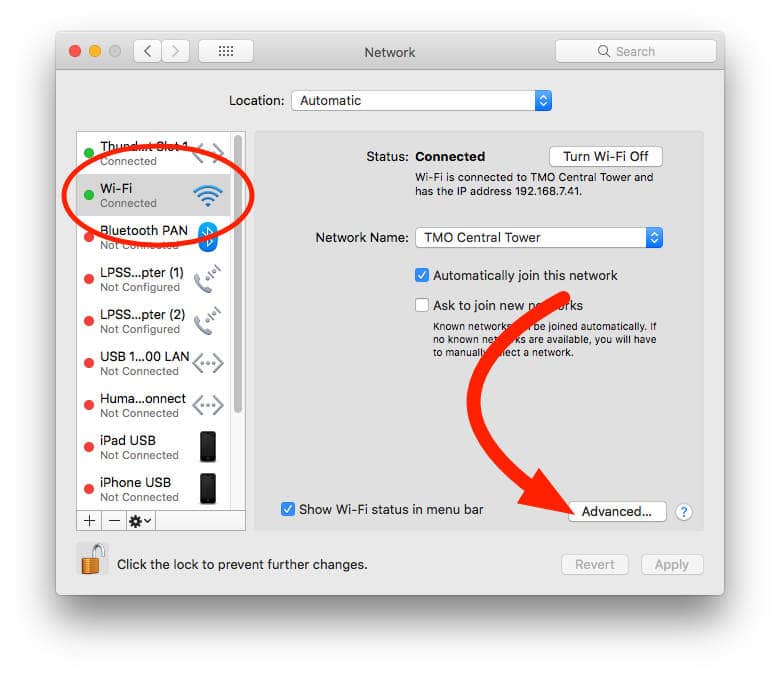
If you're using network locations because you want each location to prefer a different network service (such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet) when connecting, follow these steps to change the service order (also known as port priority) in each location.
- Choose Apple menu > System Preferences, then click Network.
- Use the Location menu to choose the location you want to modify.
- Click below the list of services, then choose Set Service Order.
- Drag services within the list to change their order. Your Mac will try to connect to the service at the top of the list first, then continue in descending order until a connection is successful.
Virtual private network (VPN) connections can't be reordered, because they always take priority over other connections. - Click OK, then click Apply to make the updated service order active.
How to prevent a network service from being used
By default, the location named Automatic makes all available network services (also known as ports or network interfaces) active, whether or not they are being used to connect to a network. Your Mac automatically searches these services for a network or Internet connection. For example, you might use a Wi-Fi network at home but an Ethernet network at work. Your Mac automatically detects which of these network services to use when it connects.
If you want to make sure that your Mac doesn't use a particular network service, such as Wi-Fi, you can make that service inactive in any of your network locations:
- Choose Apple menu > System Preferences, then click Network.
- Use the Location menu to choose the location you want to modify.
- Click below of the list of services, then choose Make Service Inactive.
- Click Apply.
You must perform additional network configuration on SuSE. You need not perform this procedure for the systems that run SLES 10 or later. By default, SLES 10 uses udev to achieve persistent interface names. Refer to the OS documentation for information on configuring persistent interfaces on SLES 10.
In rare cases where RedHat does not automatically configure the network interfaces, RedHat users may also have to perform the network configuration.
Review the following tasks that allow VCS to function properly:
VCS must be able to find the same network interface names across reboots.
VCS must have network interfaces up before LLT starts to run.
Network Configuration For Mac Windows 7
Symantec suggests the following steps for configuring network interfaces on SUSE.
Note: | You must not reboot the system between configuring the persistent interface names and configuring the interfaces to be up before starting LLT. |
Note: | The MAC address in the ifcfg-eth-id-mac file can be in uppercase or lowercase. SUSE, and therefore the Veritas product installer, ignores the file with lowercase MAC address if the file with uppercase MAC address is present. |
To configure persistent interface names for network devices
Navigate to the hotplug file in the /etc/sysconfig directory:
Open the hotplug file in an editor.
Set HOTPLUG_PCI_QUEUE_NIC_EVENTS to yes:
Run the command:
Make sure that the interface name to MAC address mapping remains same across the reboots.
Symantec recommends adding the PERSISTENT_NAME entries to the configuration files for all the network interfaces (including the network interfaces that are not used).
For each ethernet interface displayed, do the following:
If a file named /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth-id-mac, where mac is the hardware address of that interface, does not exist, then do the following:
Create the file.
If a file exists for the same network interface with the name /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-ethX, then copy the contents of that file into the newly created file. The variable ethX represents the interface name.
Add the following line at the end of the file /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth-id-mac.
where ethX is the interface name.
For example:
If a file named etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth-id-00:02:B3:DB:38:FE does not exist, do the following task:
Create the file.
If the file /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth0 exists, then copy the contents of this file into etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth-id-00:02:B3:DB:38:FE.
Add the following to the end of the file named etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth-id-00:02:B3:DB:38:FE,
Perform the procedure for all the interfaces that the ifconfig -a command displays.
Network Configuration For Mac Mojave
To configure interfaces to be up before starting LLT
Network Configuration File Mac
For each network interface that you want LLT to use, find its MAC address by running the ifconfig command:
Where eth0 is the sample network interface name. The output displays 00:0C:0D:08:C4:32 as the interface's MAC address.
Navigate to the config file in the /etc/sysconfig/network directory:
Open the config file in an editor.
Append the string eth-id-macaddress to the MANDATORY_DEVICES list in the config file. Separate each address with a space, for example:
